What is Cybersecurity Risk?
Definition, Assessement, and Strategies to Strengthen Organizational Resilience in 2025
Cybercriminals are aware of this, and they’re leveraging it to their advantage. From ransomware attacks to data breaches via misconfigured cloud services, they are finding new ways to infiltrate organizations indirectly. And with sensitive customer data, intellectual property, and financial information on the line, the stakes have never been higher.
The inclusion of third and fourth-party vendors into business operations requires organizations to adopt an extended multilayered cybersecurity strategy. An organization must prioritize these factors because they form the basis of creating an effective cybersecurity risk management strategy which protects both internal weaknesses and the security of third and fourth-party vendors’ services.
This post explores the evolving nature of cybersecurity risk and everything you need to ensure the security of your business.
What Is Cybersecurity Risk?
Cybersecurity risk refers to the potential for loss or damage to an organization’s digital assets, operations, or reputation as a result of cyber threats. These risks may originate from vulnerabilities in hardware, software, networks, or even human behavior, which can be exploited by threat actors such as hackers, criminal organizations, or malicious insiders.
The formula for assessing cybersecurity risk is often expressed as:
Risk = Threat × Vulnerability × Impact

This simple equation highlights three key elements:
Threats – These are the actors or forces that could cause harm. Security threats within cybersecurity exist as three major attack types ie:
- Social engineering attacks which exploit human vulnerabilities to extract secrets
- Service availability disruption through DDoS (Distribution Denial of Service).
- Advanced persistent threats.
Security threats exist in various forms and countries at multiple levels from within internal organizations and across external criminal organizations.
Vulnerabilities – The weaknesses that make a system exploitable. The security system contains vulnerabilities which represent points where attackers can utilize weaknesses or gaps to breach the system. The absence of security exists because systems operate with outdated software and unpatched systems and include configuration errors. Successful management of vulnerabilities remains essential to protecting organizations against their weaknesses. Continuous vulnerability scanning followed by impact evaluation and immediate system maintenance through patching and reconfiguration practices, helps mitigate attacks on security vulnerabilities.
Impact – The potential damage or consequence if the threat succeeds. Various impacts spread from cybersecurity breaches throughout many areas of operation. The actual financial consequences which result from network interruptions or data intrusions constitute the consequences. A breach has two types of negative effects: direct financial losses from ransomware activities and indirect damage to reputation which results in customer distrust. Both operational interruptions and regulatory fines that arise from non-compliance act as additional impacts. The attack sensitivity together with organizational response capability determine the severity of resulting consequences.
Understanding each of these pillars is essential to building an effective cybersecurity risk management strategy.
Types of Cybersecurity Attacks That Drive Risk
Let’s take a closer look at the most prevalent types of cyberattacks that contribute to risk:

1. Phishing Attacks
Still the most common form of attack. These fraudulent emails trick users into giving away credentials or downloading malware. Spear-phishing—a more targeted version—uses personal information to seem more credible.

3. Malware and Trojans
Attacks through these programs occur by concealing themselves in downloaded files and attachments as they spy, steal or destroy data. Trojans disguise themselves as legitimate software to bypass defenses.

5. Zero-Day Exploits

2. Ransomware
This malicious software locks files or entire systems until a ransom is paid. In recent years, healthcare, education, and municipal sectors have been frequent targets. Double-extortion techniques now threaten to leak stolen data as well.
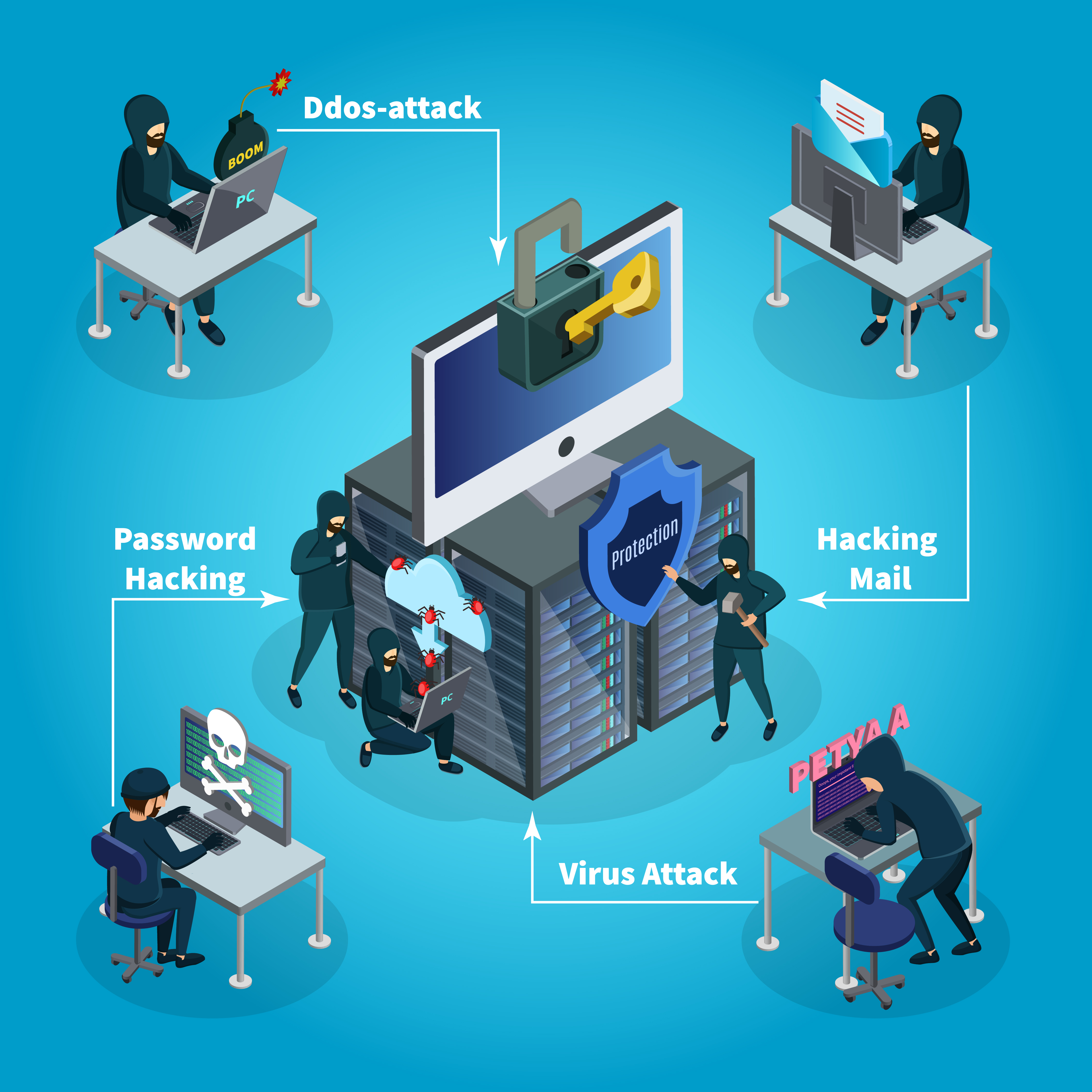
4. Denial of Service (DoS) Attacks

6. Insider Threats
How to Assess Cybersecurity Risk
The foundation of successful cybersecurity risk management requires organizations to establish complete digital environment understanding and identify their point of exposure. The nature of risks transforms continually because technology develops alongside business strategies and the professional skills of attackers. Cybersecurity risk assessment needs a strategic systematic approach because it brings operational confidence alongside essential compliance requirements for establishing long-term organizational resilience.
Risk assessments form the base of this security process. The evaluation process entails a comprehensive investigation of your organizational systems as well as processes and collaborations for discovering unknown weaknesses and business-related risks. Attackers from state nations and internal employees and digital criminals use multiple weaknesses in the digital domain to achieve their aims. The detection of weaknesses in systems occurs through outdated software combined with poor cloud management configurations and insecure Internet-of-Things devices.
To deliver meaningful results a risk assessment requires visibility of exposures which get properly quantified before assigning values to business assets. The implementation of actual data prevents your assessment from becoming obsolete by incorporating modern dangers accurately.

Cybersecurity risk assessment continues throughout organizations as an active discipline because it needs strategic analysis along with standardized tools alongside continuous executive oversight. The size of your organization and digital footprint expansion requires your organization to increase its capacity to identify and handle emerging risks. Your organization will evolve from defensive postures to proactive security resilience by implementing correct analytic methods in combination with framework conformance and organizational governance frameworks.
3 Cybersecurity Strategies that can Strengthen Organizational Resilience in 2025
1. Incident Response
Why is incident response crucial in cybersecurity? — When a cyber incident hits, there’s no time for confusion. An incident response plan drafted for readiness provides organizations with specific procedures that explain detection methods and containment strategies and recovery protocols. Corporate compliance should not be treated as a static requirement yet serves as the backbone for preserving daily operations together with customer trust while minimizing potential dangers.

2. Employee Training
What role does employee training play in cybersecurity risk management? — The greatest security vulnerability comes from human errors despite implementing sophisticated security tools. Training staff members continuously remains vital for security purposes. A properly trained staff team will detect warning signs which include problematic links as well as phishing schemes and abnormal system activities to perform correct action.

3. vCISO Services
The Virtual Chief Information Security Officer (vCISO) service provides your organization with top-level security leadership at a fraction of full-time employee expenses. Through their role a vCISO links business targets with cybersecurity approaches by leading incident response planning and policy creation and vendor risk assessment. One of the biggest benefits? Perspective.


Recent Comments